The study of the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter is called spectroscopy. Electromagnetic radiation, which is characterized by components such as wavelength, frequency and speed, has a dual property of particle and wave.
The study of the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter is called spectroscopy. Electromagnetic radiation, which is characterized by components such as wavelength, frequency and speed, has a dual property of particle and wave. In fact, electromagnetic radiation can be considered as separate particles called photons, whose energy is proportional to the radiation frequency. The electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves to gamma rays, which are called by different names according to their frequency. In ultraviolet/visible spectroscopy, the absorption of electromagnetic radiation causes the electrons of the valence layer of atoms and molecules to be excited. These electron transfers in atoms cause a number of narrow absorption lines, but in molecules they give continuous and broad absorption peaks.
What Spectroscopy Follows:
spectroscopy, with a diverse set of different laboratory methods, seeks to answer questions about topics such as molecular structure, bond lengths and energies, electron energy levels, nuclear arrangement, Rotation of molecules and...
Studying the interaction of each specific region of the spectrum of electromagnetic waves gives us specific information about the sample.
Spectroscopy is a science that studies the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter. In such interactions, electromagnetic radiation can be seen as a set of separate energy packets called photons. considered Also, in addition to particle properties, electromagnetic radiation also has wave properties. This dual characteristic of electromagnetic radiation as a particle and a wave is not only contradictory to each other but also complementary to each other. According to the wave theory, electromagnetic radiation is made of two components: electric field and magnetic field. These fields are propagating the wave in the environment, perpendicular to each other and also to the direction of the wave
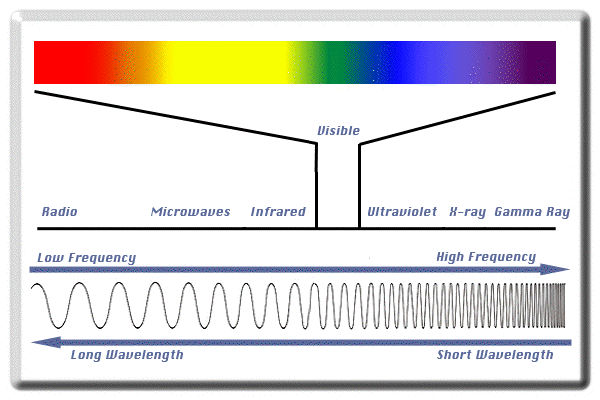
Quantitative and qualitative studies conducted as a result of substance interactions with electromagnetic radiation are called spectrochemical analyses. In general, these analyzes deal with a wide range of frequencies. This range includes radio waves to gamma rays. Electromagnetic waves can be called by different names according to their frequency: radio waves, microwave, infrared, visible light, visible light, and ultraviolet. X-ray and gamma ray. These names are arranged in order of increasing frequency (decreasing wavelength).
