Scientists, including astronomers, physicists, and chemists, use special tools to evaluate the properties of elements, objects, or materials that emit light. For example, each of these produces unique frequencies and wavelengths of light that are detected and measured by a spectrometer. Some studies take this step a step further and use a spectrophotometer to analyze the intensity of the wavelengt
Scientists, including astronomers, physicists, and chemists, use special tools to evaluate the properties of elements, objects, or materials that emit light. For example, each of these produces unique frequencies and wavelengths of light that are detected and measured by a spectrometer. Some studies take this step a step further and use a spectrophotometer to analyze the intensity of the wavelengths and compare them to a standard source.
A spectrometer is an instrument that scientists use to gather information about a substance based on the visible, ultraviolet, or infrared light it produces, and it can be used in a variety of scientific fields. For example, astronomers use spectrometers to find the temperature of an object in space, measure its speed, and even estimate its weight. Scientists also use spectrometers to determine the composition of materials on Earth or in space. It contains the basic components of the items. Scientists in the medical field often use spectrometers to detect pollutants, toxins in the bloodstream, or even diseases.
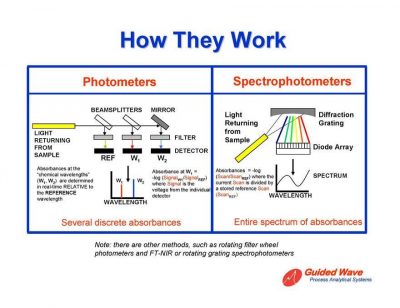
A spectrophotometer is a device used to measure the intensity of electromagnetic radiation at different wavelengths. Spectrophotometers are used to measure the absorbance of a certain wavelength of a solution, reflectance of solutions, transmission or transparency of solids. In addition, they also measure the penetration of the light spectrum in the electromagnetic radiation spectrum, which covers about 200 nm to 2500 nm with various calibrations and controls. Spectrophotometer has two basic classifications. The first type is the double-beam spectrophotometer , which compares the light intensity between a reference light path and the material being measured. The second type is a single beam spectrophotometer that measures the relative light intensity of the beam before and after introducing the test sample.
